Herzliya Medical Center
Tel: +972-9-959-4888
09:00-18:00
 Treatment of Hirschsprung’s disease in children is performed by pediatric specialists at Herzliya Medical Center in Israel. The most advanced methods of treatment for Hirschsprung’s disease in Israel are utilized and paired with highly effective postoperative treatment for rehabilitation, allowing patients to return to a normal lifestyle within a short period.
Treatment of Hirschsprung’s disease in children is performed by pediatric specialists at Herzliya Medical Center in Israel. The most advanced methods of treatment for Hirschsprung’s disease in Israel are utilized and paired with highly effective postoperative treatment for rehabilitation, allowing patients to return to a normal lifestyle within a short period.
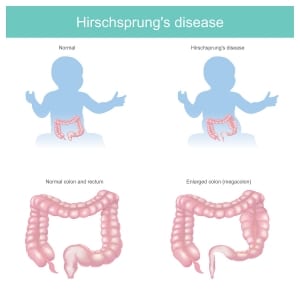
Healthy bowel functions from the wavelike contraction of the smooth muscle – known as peristalsis. Ongoing peristalsis promotes intestinal health and absorption of fluid and nutrients; a necessary process in conjunction with the evacuation of feces. Hirschsprung’s disease is characterized by a congenital defect in the structure of nerve endings (lack of nerve ganglia) in the smooth muscles of the colon, which disturbs motor function. Motility disorders can lead to severe constipation, this may result in complete intestinal obstruction, along with other complications that may be life-threatening. The disease is hereditary and associated with the presence of other genetic mutations. Hirschsprung’s disease predominantly occurs in males and often observed among patients suffering from other hereditary diseases.
Various forms of Hirschsprung’s disease depend on the location of the intestinal lesion, removal of a short segment of the colon. In the colon, distal portions, such as the rectum and sigmoid are most affected. The removal of the short segment of the colon is known to be the most commonly diagnosed form of Hirschsprung’s disease (75% of patients).
Depending on the clinical course established, experts distinguish each patient’s development of Hirschsprung’s disease into two categories: compensated (stable) and decompensated (complicated)
Symptoms of Hirschsprung’s disease are observed in infancy and early childhood. For 80% of patients, symptoms of the disease develop during the first weeks and months of life. In rarer cases, children are diagnosed much later (6-10 years). Symptoms of Hirschsprung’s disease are characterized by:
Disease severity is clinically diagnosed thorough evaluation of the health of the colon, timely diagnosis, and the extent of symptomatic treatment that has been conducted. Severe cases of Hirschsprung’s disease have led to the development of toxic megacolon, sepsis (blood poisoning), and intestinal obstruction. Hirschsprung’s disease patients exhibiting such complications require emergency medical intervention.
At HMC in Israel, various diagnostic tools are used to screen for Hirschsprung’s disease as early as possible:
Symptomatic therapy, including adherence to a strict diet, is often paired with the use of laxatives and cleansing enemas, but provide only a temporary effect. The vast majority of patients require surgical treatment.
Surgical Procedures for Hirschsprung’s disease involves the removal of the affected area of the colon. The procedure is performed in one or two stages:
In the Department of Pediatrics at Herzliya Medical Center in Israel, several surgical options for treatment of Hirschsprung’s disease are made available to patients. Services are delivered to patients by a multidisciplinary team of pediatric professionals that work to provide comprehensive care aimed at full restoration of bowel function and to prevent complications. Early treatment that is timely and effective provides patients with the opportunity to achieve favorable prognosis among many cases of the disease.