Herzliya Medical Center
Tel: +972-9-959-4888
09:00-18:00
Cancer of the cervix is cancer that begins in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. This cancer occurs when the cells of the cervix grow abnormally and invade other tissues and organs of the body.
It tends to occur in midlife and is most frequently diagnosed in women between the ages of 35 and 44, and rarely develops in women younger than 20.
Treatment in Israel is based on the results obtained by the diagnosis and the individual wishes of the patient.
A common cause of the disease is an infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is sexually transmitted.
Thus, one way of prevention is to receive HPV vaccines capable of protecting against this type of viruses.
In addition, early sexual contact, multiple sexual partners, and taking oral contraceptives (birth control pills) increase the risk because they lead to greater exposure to HPV.
It’s important to know that cancer of the cervix often has no symptoms in its early stages.
As the disease progresses, these signals of a possible incidence of cervical cancer may appear:
If you are experiencing one or more of these symptoms, you should make an appointment today.
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that concern you.
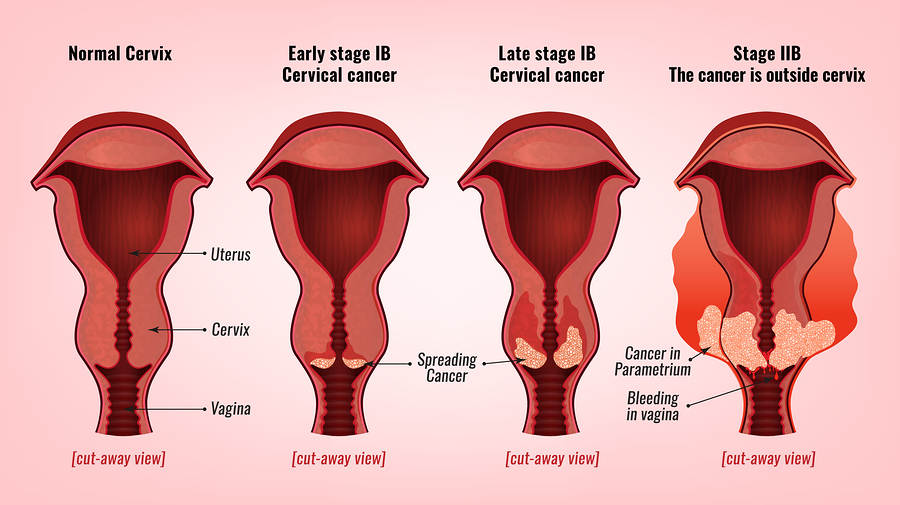
Staging aims to assess how far cancer has spread and whether it has reached nearby structures or more distant organs.
Early detection has a positive effect on the success of the therapy. The Pap test can detect precancerous conditions of the cervix.
Our Laboratory does further examination under a microscope for the presence of abnormal cells and dysplasia.
The cervical cancer death rate dropped significantly with the increased use of this test.
DNA testing for HPV (human papillomavirus) is used as a follow-up to abnormal changes traced with a Pap smear.
The DNA test reveals the carrier types of HPV that can trigger the development of this kind of cancer. If clinical signs and the presence of abnormal cells in the course of screening is detected, additional checks are necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Cancer of the cervix is divided into two main types:
The diagnosis includes:
On detecting cervical cancer, the patient goes under further diagnostic tests for defining the extent of the cancer process. Usually, you will be asked to do screening tests such as X-ray, CT, MRI, and PET. Additional tests may be required such as cystoscopy.
The treatment structure depends on the stage of cancer, the patient’s chronic disease history, and her preferences. The treatment is complex and usually includes surgery during which a full or partial excision of the uterus (hysterectomy) is performed.
Hysterectomy surgery in the initial stages of this cancer is a highly effective therapy, which is capable of preventing the recurrence of the disease.
Combine to the surgery, you will be recommended to receive:
If you suspect any of the signs above or were diagnosed for cervical cancer, we here, at our Private Hospital creates ideal conditions for the diagnosis and treatment of all cervical cancer disease. HMC successful recovery rates of cervical cancer due to its professional oncologists working in a modern environment.