Herzliya Medical Center
Tel: +972-9-959-4888
09:00-18:00
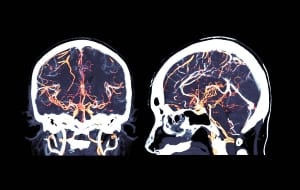 The world of catheterizations is advancing at a great pace in recent years and offers abilities allowing to perform, even though one tiny incision, a variety of actions that used to be possible only with open surgery. An excellent example of that is Cerebral angiography, which today allows the treatment of urgent problems and insignificant cases like a cerebral aneurysm, as well as examining and diagnosing the delicate and sensitive blood vessels in one of the most important organs in our body.
The world of catheterizations is advancing at a great pace in recent years and offers abilities allowing to perform, even though one tiny incision, a variety of actions that used to be possible only with open surgery. An excellent example of that is Cerebral angiography, which today allows the treatment of urgent problems and insignificant cases like a cerebral aneurysm, as well as examining and diagnosing the delicate and sensitive blood vessels in one of the most important organs in our body.
At the Herzliya medical center hospital, there are new generation catheterization rooms, in which thousands of procedures taken place every year, among there also Cerebral angiography. The catheterizations at the hospital are performed by the finest and top doctors in the world in the field, like Dr. Shimon Mimon, an invasive neuroradiologist (Cerebral angiography) and diagnostic neuroradiologist.
Cerebral angiography is a procedure allowing direct access to the brain’s blood vessels. There is diagnostic catheterization, designed to closely deal with different blood vessels in the brain, and there is Coronary Angioplasty, during which phenomena or diseases related to blood vessels in the brain can be treated. At the Herzliya medical center hospital, diagnostic Cerebral angiography is performed as well as Cerebral angiography for treatment of cerebral aneurysm (AVM) or – conditions where blood vessels are expanding in a specific spot and could burst and tear, leading to life-threatening cerebral bleeding. In the not so distant past, treatment of cerebral aneurysm was done only within open surgery – meaning through a hole made in the head and skull. Today, almost all cases of cerebral aneurysm are treated by Cerebral angiography, because it is simpler, quicker and ensures the patient’s shorter and much faster recovery.
At the base of it, Cerebral angiography is performed like any other catheterization: through a main artery in the body, a catheter is inserted – a long and thin tube. Through the catheter, different medications can be injected directly into the treated area, specific blood vessels can be expanded and stents inserted.
However, the differences between Cerebral angiography and other catheterizations are quite big. It should be remembered that cerebral blood vessels are more sensitive, smaller and have delicate anatomy: they aren’t protected and covered by muscle and tissue, as opposed to blood vessels going into the heart, for example, so it’s easier to hurt and tear them. Therefore, the device with which Cerebral angiography is performed must be especially small and delicate.
And indeed, the catheter the doctor uses will be especially thin: the diameter of the conductor penetrated to the cerebral blood vessels is only 0.07 inches. The thickness of the catheter used in cardiac catheterizations, for example, is twice as large.
The catheter used in Cerebral angiography is inserted through the femoral artery or the internal iliac artery – 2 arteries that are considered fairly wide. That catheter is lead up to the neck, at which point the conducting catheter, the thinnest, leaves it, and continues the course from the neck to the problematic blood vessel in the brain.
In the event of catheterization due to cerebral aneurysm, a special coil, or several coils, will be lead through the catheter to the point where the aneurysm took place. The coils will be placed in the problematic points and prevent blood flow to the aneurysm, leading to its collapse.
In parallel to the Coronary Angioplasty, the treated area is also photographed via Angioplasty imaging (usually CT or, MRI) to allow the doctor to easily see the problematic blood vessel and make sure the action was performed properly.
This imaging is also used for a general inspection of the blood vessels in the brain, prior to the catheterization. Thus, problematic blood vessels can be located, where an aneurysm could develop in the future, allowing the catheterizing doctor to strike first and treat the blood vessel before it is damaged.
Therapeutic Cerebral angiography takes between 2 and 3 hours. diagnostic catheterization might be shorter. Usually, after the catheterization is successfully completed, the patient will be moved to intensive care supervision overnight, after which he will stay at the hospitalization room for another 2 days. Afterward, he’ll be discharged, according to of course to the patient’s condition and the degree of the damage to his brain, if any, due to the problem leading him to the hospital.
Catheterization rooms at the Herzliya medical center hospital are considered the most advanced and modern in Israel. knowing you are being treated by the finest catheterizing doctors in the world, alongside the most advanced equipment, professional helpful staff, and the finest hospitalization conditions the hospital offers, contribute to the success of the process and its optimal performance.
The article was written in cooperation with Dr. Shimon Mimon, a top invasive neuroradiologist (Cerebral angiography) and diagnostic neuroradiologist at the Herzliya medical center hospital.